tiger-algebra-calculator
அணுவின் மாசத்தை கண்டறியும் முறை
அணு மாசம்
அணு மாசம் (அதன் மாசத்தை, பூர்மைக் கூறு மாசை, மாச நிவான கூறையும் ம் அல்லது பூர்மைக் கூறு மாசையும் என்றும் பார்க்கப்படுகின்றது) ஒர் மூலகத்தை உருவாக்கும் அணுவின் மாசங்களை மேலும் இணைத்த சேர்க்கையினால் கிடைக்கும். அது ஒவ்வொரு மூல அணுவின் மாசங்களை அவற்றின் மாசத்தால் பெருக்கி மொத்தத்தில் சேர்த்து மாசத்தை கண்டறிய முடியும்.For example, contains two Hydrogen atoms, each with an atomic weight of 1.008u, and one Oxygen atom with an atomic weight of 15.999u. To find the molecular mass of , we multiply Hydrogen's atomic weights by 2, because there are two Hydrogen atoms in and we need to find their combined mass, and add it to the atomic weight of Oxygen, because there is only one Oxygen atom in , to get 18.015u.
அணு மாசம் ஒருதனித்த அணு மாச அலகுகளில் அளக்கப்படுகின்றது, இதை u என்கிற குறிப்பில் சுட்டிக்காட்டப்படுகின்றது. இவற்றை amu ஆகிய முந்தைய குறிப்புக்கு முதன்முதலில் எழுதியது மிகவும் பொதுவானது அல்லது Dalton அலகுகளில், அதுவே Da என்று சுட்டிக்காட்டப்படுகின்றது.
சார்ந்த திட்டங்கள்:
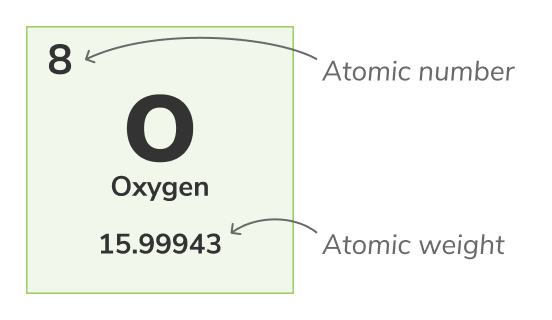
Atomic number
Atomic number - (also called proton number) the number of protons found in the nucleus of every atom of a chemical element. It uniquely identifies a chemical element, for example, all atoms of Oxygen have 8 protons. The atomic number is usually shown above the elements in the periodic table.Mass number
Mass number - (also called atomic mass number or nucleon number) refers to the total number of protons and neutrons (together known as nucleons) in an atomic nucleus. One element can have different types of isotopes. For example, Oxygen can have a mass number of or . All it's isotopes have protons but different number of neutrons, or respectively.Atomic mass
Atomic mass or - is the mass of an atom. the numeric value of the atomic mass of an atom is nearly the same as its mass number value. For example, the mass of Oxygen- is 15.99491461956 u.Atomic weight
Atomic weight - (also called standard atomic weight) is the average weight of all an atom's natural isotopes. Because isotopes vary in weight, standard atomic weight is calculated by taking the average of the masses of all of an atom's isotopes. For example, Oxygen (O-16) atoms are 99.762% of all Oxygen atoms, Oxygen (O-17) atoms are 0.038% of all Oxygen atoms and Oxygen (O-18) atoms are 0.2% of all Oxygen atoms. The atomic weight of Oxygen is the average of its 3 isotopes and is equal to 15.99943 uThe atomic weight is represented by the lower number in the periodic table.