टाइगर बीजगणित कैलकुलेटर
दीर्घवृत्तों के गुण
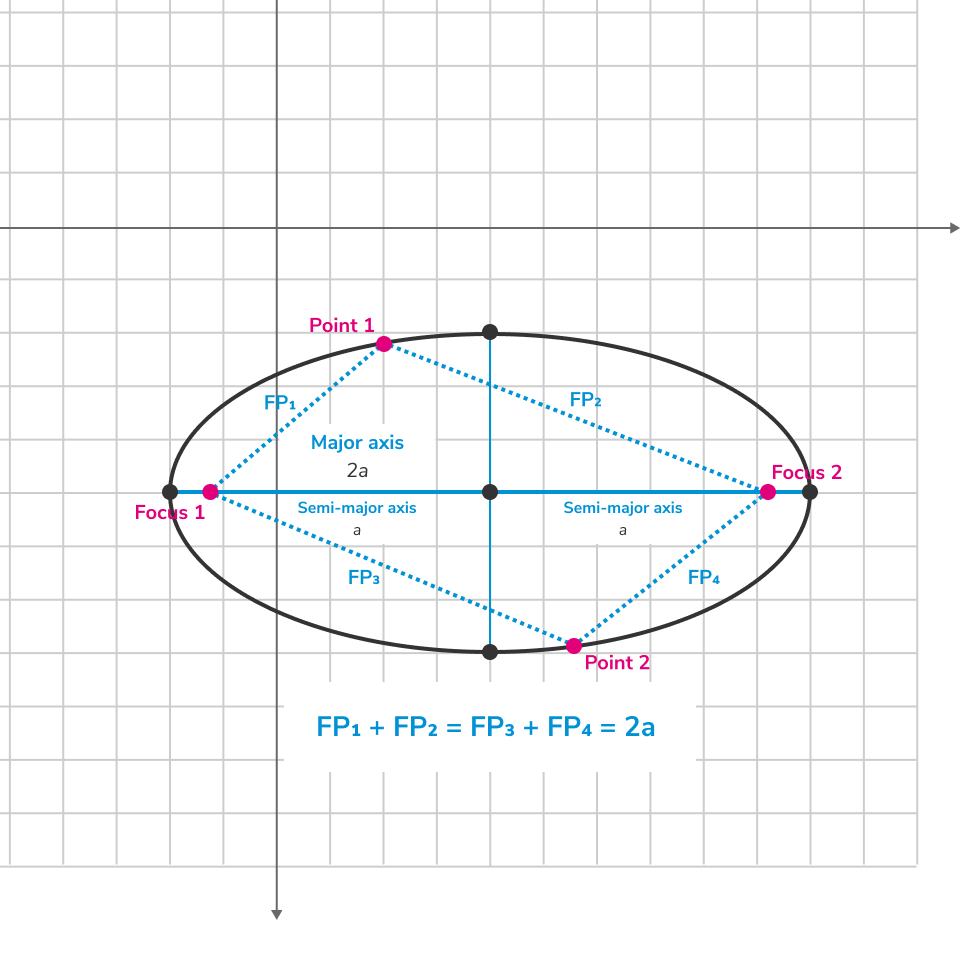
एलिप्स उन सभी बिंदुओं का समूह है जो एक समतल पर होते हैं, जिनकी दूरियां दो ठोस बिंदुओं, जो फोकस प्वाइंट्स या फोकाई कहलाते हैं, से एक स्थिर मान के बराबर होती है जो एलिप्स के मुख्य धुरी की लंबाई के बराबर होती है।
उदाहरण के लिए, मान लीजिए कि हमारी पास इकाइयों लंबी मुख्य धुरी है। एलिप्स के फोकाई हमेशा मुख्य धुरी पर स्थित होते हैं। एलिप्स स्वयं की अनुमानित रेखाओं के द्वारा स्थापित होता है, जो दोनों फोकाई से एलिप्स पर एक ही बिंदु के लिए, ऐसे होते हैं कि उनकी कुल लंबाइयाँ के बराबर होती हैं, जो मुख्य धुरी की लंबाई होती हैं। रेखाओं की लंबाइयाँ और , और , और हो सकती हैं या वास्तव में किसी भी संयोजन में सकारात्मक तर्कसंगत संख्याओं की हो सकती है जो के बराबर होती हैं, जिनकी संख्या अनन्त होती है।
Standard form
Note: एक ellipse के Standard form equation के दो भाग fractions होते हैं, जिनमें दो denominators में से बड़ा होता है और दोनों में से छोटा होता है। एक ellipse के Standard form की आवश्यकता होती है कि equation की right side बराबर से हो।
 Points
Points
Lines, line segments, and axes
Other properties
उदाहरण के लिए, मान लीजिए कि हमारी पास इकाइयों लंबी मुख्य धुरी है। एलिप्स के फोकाई हमेशा मुख्य धुरी पर स्थित होते हैं। एलिप्स स्वयं की अनुमानित रेखाओं के द्वारा स्थापित होता है, जो दोनों फोकाई से एलिप्स पर एक ही बिंदु के लिए, ऐसे होते हैं कि उनकी कुल लंबाइयाँ के बराबर होती हैं, जो मुख्य धुरी की लंबाई होती हैं। रेखाओं की लंबाइयाँ और , और , और हो सकती हैं या वास्तव में किसी भी संयोजन में सकारात्मक तर्कसंगत संख्याओं की हो सकती है जो के बराबर होती हैं, जिनकी संख्या अनन्त होती है।

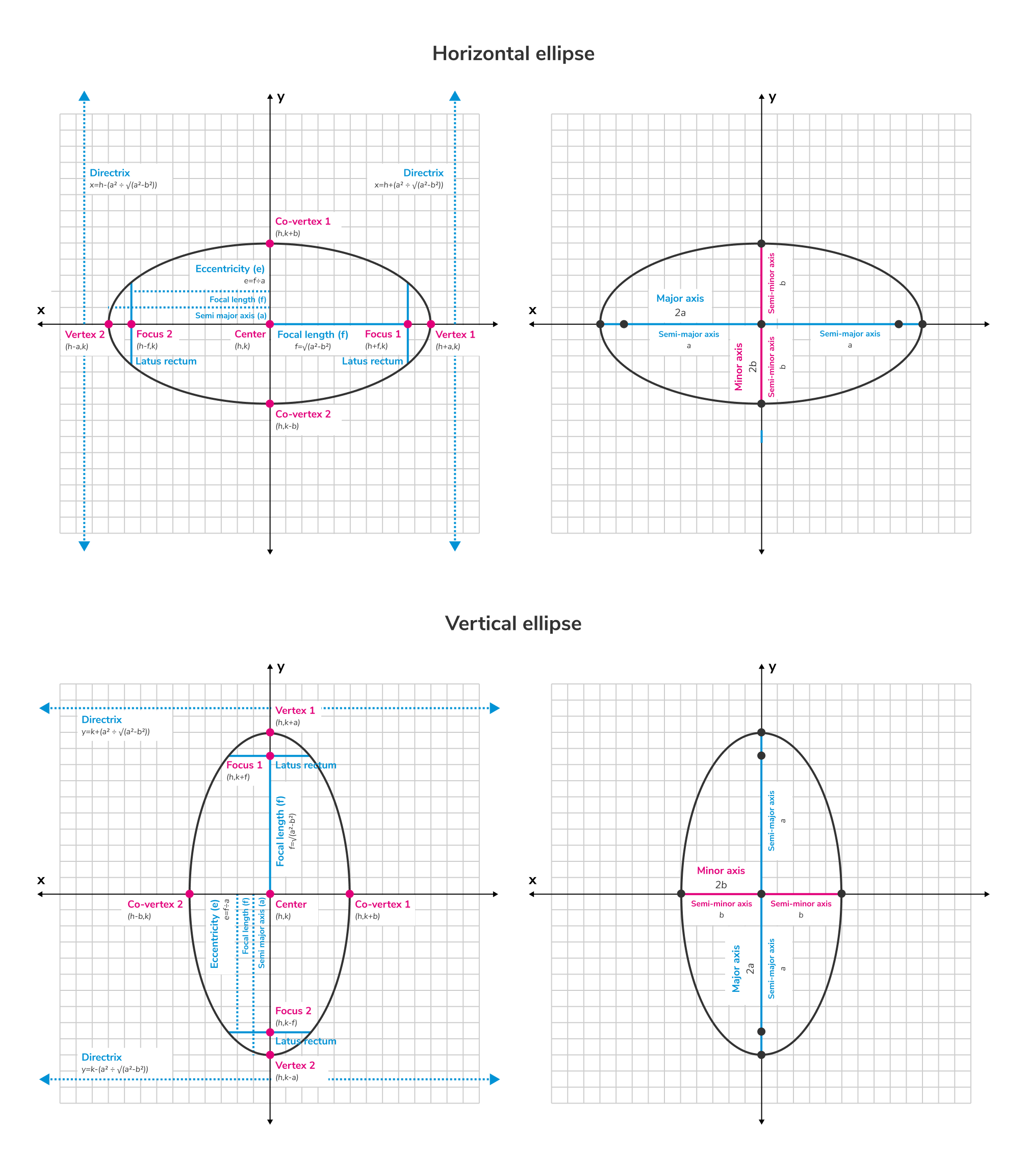
Standard form
- Horizontal ellipse का Standard form:
- Vertical ellipse का Standard form:
Note: एक ellipse के Standard form equation के दो भाग fractions होते हैं, जिनमें दो denominators में से बड़ा होता है और दोनों में से छोटा होता है। एक ellipse के Standard form की आवश्यकता होती है कि equation की right side बराबर से हो।
 Points
Points
- Center : ellipse के center में एक point. ने x-coordinate को प्रतिष्ठित किया और ने y-coordinate को प्रतिष्ठित किया।
- Vertices: Major axis के संघर्षों को ellipse के साथ।
- Co-vertices: Minor axis के संघर्षों को ellipse के साथ।
Lines, line segments, and axes
- Major axis : एक ellipse बनाने वाले दो axes में से लंबा। यह ellipse की एक ओर से, उसके center के माध्यम से, सबसे चौड़े बिंदु पर दूसरी ओर जाता है।
- Minor axis : एक ellipse बनाने वाले दो axes में से छोटा। यह Major axis के लंबाई को आधा करता है, एक ओर से ellipse के center के माध्यम से, दूसरी ओर।
- Semi-major axis : Major axis की लंबाई का आधा।
- Semi-minor axis : Minor axis की लंबाई का आधा।
- Focal length : एक ellipse के center से उसकी एक फोकस तक की दूरी।
- Focal parameter : एक focus से corresponding directrix तक की दूरी।
- Directrix: Two lines outside of the ellipse that run perpendicular to the major axis and are used in conjunction with the foci to define the ellipse.
In a horizontal ellipse:
In a vertical ellipse: . - Latus rectum: The line segments that run perpendicular to the major axis, through the foci, such that their endpoints lie on the ellipse. Their lengths equal .
Other properties
- Area:
- Eccentricity : A measure of how elongated an ellipse is, defined by the following ratio: 1. The distance from the center to either focus to 2. The distance from the center to either vertex:
The eccentricity of an ellipse is always between and .
