টাইগার এলজেব্রা ক্যালকুলেটর
সমন্বয়ী তলে একটি অর্ডার যুগল চিত্রণ
অর্ডার যুগল
মিলে নির্দিষ্ট করা এবং গুলি এই ধরনের ওজনের সাধারণ ধরণ। বিভাজ্যের ধরণের মাধ্যমে এবং বিন্যাসিত স্থানের নিচে অবস্থান নির্দিষ্ট করে।
এবং এবং এবং এর নির্দিষ্ট কার্যের অর্ধেক যে কোনও সংখ্যার ব্যবহার হবে, তা নির্দিষ্ট হবেনা।
সমন্বয়ী তলমিলে নির্দিষ্ট করা এবং গুলি এই ধরনের ওজনের সাধারণ ধরণ। বিভাজ্যের ধরণের মাধ্যমে এবং বিন্যাসিত স্থানের নিচে অবস্থান নির্দিষ্ট করে।
এবং এবং এবং এর নির্দিষ্ট কার্যের অর্ধেক যে কোনও সংখ্যার ব্যবহার হবে, তা নির্দিষ্ট হবেনা।
বিন্যাস
Quadrant I (top right): both x and y-coordinates are positive.
Quadrant II (top left): x-coordinate is negative; y-coordinate is positive.
Quadrant III (bottom left): x-coordinate is negative; y-coordinate is negative.
Quadrant IV (bottom right): x-coordinate is positive; y-coordinate is negative.
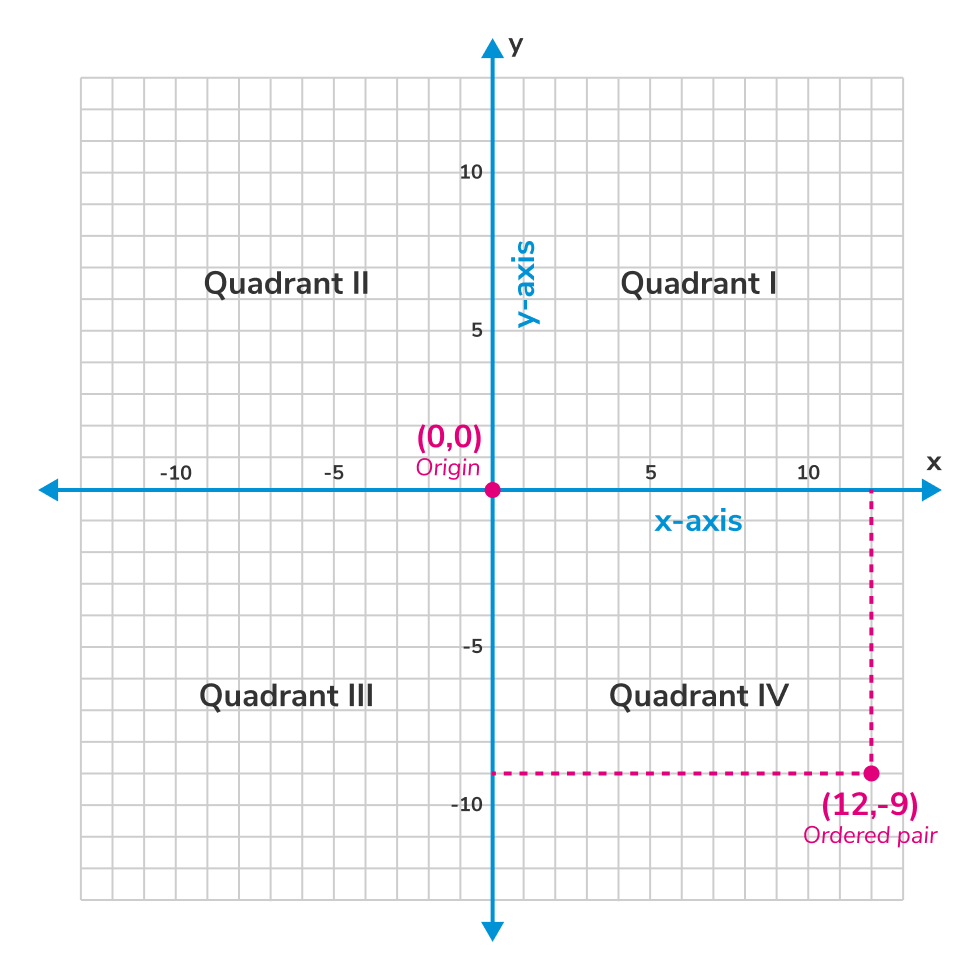
Points with at least one coordinate that equals are located on the x or y-axis, meaning they are not in any quadrant. Ordered pairs with the form are located on the horizontal x-axis, whereas ordered pairs with the form are located on the vertical y-axis.
Other relevant terms:
Origin: The point where the x and y-axes intersect. Its coordinates are and it represents the center of the coordinate plane.
Point: A point is a representation of an ordered pair on a coordinate plane. Though they are usually drawn as dots, points do not have dimensions and are only used to indicate location.
x-axis: One of the two number lines that form a coordinate plane. The x-axis runs horizontally (left and right).
y-axis: One of the two number lines that form a coordinate plane. The y-axis runs vertically (up and down).
Abscissa: The x-value in an ordered pair. For example: In , is the abscissa.
Ordinate: The y-value in an ordered pair. For example: In , is the ordinate।
